Warum Kunden uns wählen :
- Hersteller-Direktsteuerung
- Technische Unterstützung
- Gleichbleibende Qualität
- Verlässliche Vorlaufzeit
Carbon fiber channels are structural composite profiles manufactured by forming carbon fiber reinforcements into U- or C-shaped geometries and curing them with controlled resin systems.
These profiles combine low weight with high bending stiffness and dimensional stability, making them suitable for load-bearing and reinforcement applications where structural efficiency is critical.
Unlike flat carbon fiber sheets or decorative composite trims, carbon fiber channels are engineered structural components designed to resist bending, deflection, and localized loads.
By leveraging the open channel geometry, these profiles achieve an effective balance between stiffness, accessibility, and integration flexibility. Fiber orientation, laminate thickness, and layup strategy can be adjusted to optimize performance for specific loading directions and assembly requirements.
Carbon fiber channel profiles are typically produced using epoxy-based resin systems to achieve reliable mechanical properties and long-term durability. When properly designed, they offer excellent fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, and vibration damping compared to traditional aluminum or steel channels, particularly in weight-sensitive structures.
For industrial and OEM applications, consistent performance depends on controlled manufacturing parameters such as wall thickness uniformity, fiber distribution, and curing stability.
Material selection, layup design, and process control play a critical role in ensuring repeatable strength, dimensional accuracy, and surface quality across production batches.
Carbon fiber channels are available in multiple structural configurations to meet different load and mounting requirements.
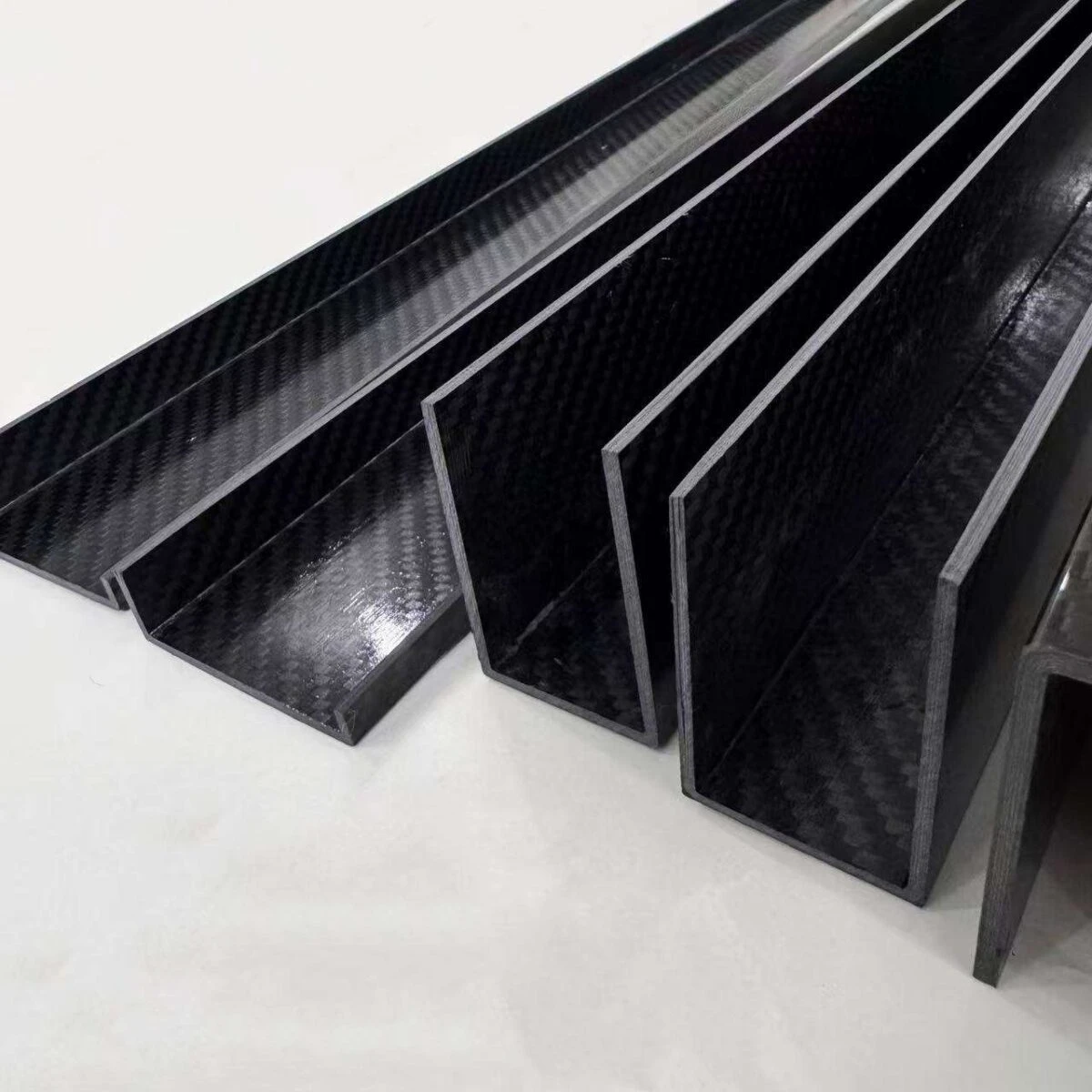
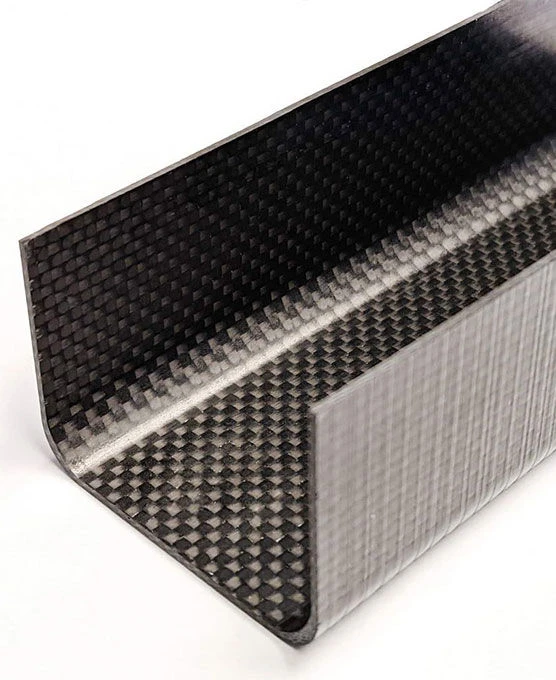
Carbon fiber U channels provide efficient bending stiffness with open-sided geometry, making them suitable for reinforcement rails, lightweight frames, and support structures that require easy integration.
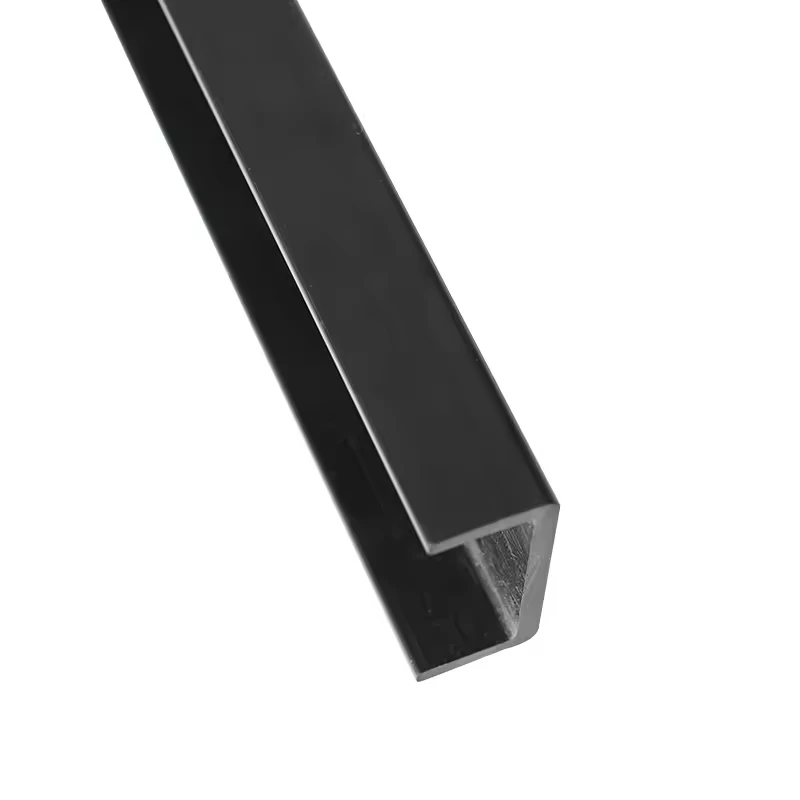
Carbon fiber C channels offer improved edge access and mounting flexibility, commonly used in modular frames and structural assemblies.

Custom channel profiles can be engineered with tailored dimensions and layup configurations to meet specific structural and assembly requirements.
Carbon fiber channel profiles are supplied based on project requirements rather than fixed catalog sizes.
| Parameter | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Channel Width | 10 – 100 mm |
| Wanddicke | 1 – 6 mm |
| Length | Up to 3000 mm |
| Fiber Orientation | Unidirectional / Multidirectional |
| Resin System | Epoxy (standard) |
| Oberflächenbehandlung | Matte, Glossy, Woven, Machined |
Carbon fiber channel profiles are commonly selected for applications requiring lightweight structural support, stiffness, and long-term durability.
Manufacturing methods are selected based on channel geometry, structural requirements, and production volume.

Pultrusion is commonly used for carbon fiber channels with constant cross sections.
This process provides stable wall thickness, consistent fiber alignment, and repeatable quality for long, straight structural channels.
Lay-up and compression molding methods are applied to channel profiles with variable dimensions, corner radii, or localized reinforcement requirements.
These processes allow greater flexibility in laminate design to match specific load paths and assembly constraints.
After curing, carbon fiber channels can be CNC machined to achieve precise lengths, slots, and mounting features.
Secondary processing ensures accurate integration into assemblies without compromising structural integrity.
Carbon fiber channels and aluminum channels are both widely used structural profiles in industrial and engineering applications. While aluminum channels have long been the standard choice, carbon fiber channels are increasingly adopted in projects where weight reduction, stiffness optimization, and long-term structural performance are critical.
Below is a practical comparison to help engineers and buyers select the appropriate channel material based on application requirements.
One of the most significant advantages of carbon fiber channels is their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio.
Carbon fiber channels deliver high tensile strength and bending stiffness at significantly lower density
Aluminum channels provide good absolute strength but require thicker or heavier sections to achieve comparable stiffness
In weight-sensitive structures such as UAV frames, robotic assemblies, and lightweight industrial equipment, carbon fiber channels can typically reduce structural weight by 30-60% compared to aluminum channels while maintaining equivalent or higher stiffness.
Carbon fiber channels can be engineered with tailored fiber orientations (0°, 90°, ±45°), allowing stiffness and strength to be optimized along specific load paths.
This makes them highly effective in applications with directional bending or torsional loads.
Aluminum channels are isotropic, meaning their mechanical properties are uniform in all directions. While this simplifies structural design, it limits the ability to optimize stiffness without increasing section size or weight.
As a result, carbon fiber channels excel in engineered, load-specific structures, whereas aluminum channels are better suited for general-purpose framing.
Carbon fiber channels are inherently resistant to corrosion, moisture, and most industrial chemicals, making them suitable for outdoor, marine-adjacent, or chemically exposed environments.
Aluminum forms a natural oxide layer that provides basic protection, but it can still suffer corrosion in saltwater, humid, or aggressive chemical conditions without additional surface treatments such as anodizing or coating.
For applications requiring long-term durability with minimal maintenance, carbon fiber channels often provide superior environmental resistance.
Aluminum channels offer excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, making them suitable for:
Strukturen zur Wärmeableitung
Electrical grounding components
Enclosures requiring thermal management
Carbon fiber channels are electrically conductive but exhibit much lower thermal conductivity than aluminum. They are not typically used where heat transfer is a primary design function.
Aluminum channels are easy to machine using standard CNC processes, offering fast cutting speeds, low tooling costs, and broad fabrication compatibility.
Carbon fiber channels require specialized machining methods, such as:
CNC machining with dust extraction
Diamond-coated or composite-specific tools
Controlled cutting parameters to prevent delamination
While fabrication complexity is higher, carbon fiber channels enable lightweight, high-precision structural components that are difficult to achieve with metal profiles.
Aluminum channels generally have lower raw material and machining costs
Carbon fiber channels involve higher upfront material and processing costs
However, in performance-driven applications, carbon fiber channels often deliver better Lebenszykluswert through reduced system weight, improved fatigue resistance, and longer service life.
| Anmeldung | Better Choice | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| UAV & aerospace structures | Kohlefaser-Kanäle | Lightweight & high stiffness |
| Robotics & automation frames | Kohlefaser-Kanäle | Directional strength & vibration resistance |
| Lightweight industrial equipment | Kohlefaser-Kanäle | Structural efficiency |
| Heat dissipation frames | Aluminum Channels | Wärmeleitfähigkeit |
| Cost-sensitive structural frames | Aluminum Channels | Lower material and machining cost |
Wählen Sie carbon fiber channels if your project prioritizes:
Lightweight structural design
High stiffness and strength efficiency
Fatigue resistance and long service life
Corrosion resistance in demanding environments
Wählen Sie aluminum channels if your project prioritizes:
Geringere Anfangskosten
Wärmeleitfähigkeit
Simple machining and high-volume production
A carbon fiber channel is a U- or C-shaped composite structural profile used for lightweight reinforcement and load-bearing applications.
They are commonly used in structural frames, UAV and robotics structures, industrial equipment, and lightweight modular assemblies.
In terms of strength-to-weight and stiffness efficiency, carbon fiber channels typically outperform aluminum channels in weight-sensitive structures.
Yes. Dimensions, wall thickness, fiber orientation, and surface finish can be customized based on application and engineering requirements.
They are typically produced using pultrusion for constant cross sections, lay-up or compression molding for complex geometries, followed by CNC machining if required.
Yes. With controlled manufacturing processes, carbon fiber channels can achieve consistent mechanical performance and repeatable quality for OEM and batch production.